Mobile-First Indexing: How to Optimize Your Website for Google's Latest Algorithm Update in 2023 Mobile-first indexing is a change in the way that Google crawls and indexes web pages. With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily uses the mobile version of a website's content for indexing and ranking, instead of the desktop version. This means that if a website doesn't … [Read more...] about Mobile-First Indexing: How to Optimize Your Website for Google’s Latest Algorithm Update in 2023
The Ultimate SEO Strategy Guide for 2023: Boost Your Website’s Rankings
The Ultimate SEO Strategy Guide for 2023: Boost Your Website's Rankings The best SEO strategy for 2023 will likely involve a combination of several tactics, as the search engine landscape continues to evolve. However, some key elements to focus on for a successful SEO strategy in 2023 may include: High-quality, relevant content: Content will continue to be a crucial … [Read more...] about The Ultimate SEO Strategy Guide for 2023: Boost Your Website’s Rankings
Link Best Practices for Better Google Ranking: Latest Strategies for 2023
How to Use Links for Better Google Ranking 2023 Links are a crucial part of any website's optimization strategy in 2023. Google uses links to crawl and index web pages, so it's essential to make sure that your links are crawlable and easy for Google to understand. Here are some best practices for using links to improve your website's Google ranking: Make your links … [Read more...] about Link Best Practices for Better Google Ranking: Latest Strategies for 2023
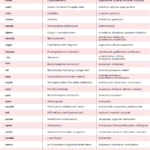
Medication Prefixes and Suffixes: A Free Cheat Sheet to Decode Common Medication Names
Medication Prefixes and Suffixes: A Free Cheat Sheet to Decode Common Medication Names The world of medications can be overwhelming, especially if you're unfamiliar with the jargon used to describe them. However, once you learn how to decode medication names, you'll have a better understanding of what they are used for and what class of drugs they belong to. This article … [Read more...] about Medication Prefixes and Suffixes: A Free Cheat Sheet to Decode Common Medication Names
Portugal Work Visa for Pakistani Citizens: Requirements and How to Apply
Portugal Work Visa for Pakistani citizens: Requirements and How to Apply Portugal is a popular destination for individuals seeking new opportunities and a better standard of living. The country is known for its scenic beauty, rich culture, and favorable business environment, making it an attractive destination for job seekers. If you are a Pakistani citizen and are … [Read more...] about Portugal Work Visa for Pakistani Citizens: Requirements and How to Apply