Tramadol Analgesic Pharmacology, Side Effects & Nursing Considerations Tramadol, a centrally acting analgesic structurally related to codeine and morphine, consists of two enantiomers, both of which contribute to the analgesic activity via different mechanisms. … [Read more...] about Tramadol Analgesic Pharmacology, Side Effects & Nursing Considerations
When You Ask Your Photographer Friend To Babysit Your Cat
When reddit user JDMcompliant’s best friend asked him to babysit her cat, Jade, for a few days he happily obliged. As a studio photographer, he also couldn’t help himself—and did a photoshoot for Jade and shared the session with the always cat-appreciate Internet. JDCompliant said he used a simple setup: Strobe light; grey wall for backdrop; shot with a Canon 6D MK2, and … [Read more...] about When You Ask Your Photographer Friend To Babysit Your Cat
The Limits of the Human Body
The Limits of the Human Body Push your characters to the limit without actually killing them off. We have an irrepressible urge to push our boundaries and set records. How much further can we go, physically and mentally, before we reach our ultimate limits? … [Read more...] about The Limits of the Human Body
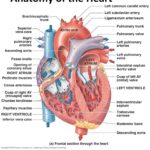
Human Heart: Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart
Human Heart: Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart Internal Anatomy of the Heart The human heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is located in the center of the chest and is about the size of a fist. The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria receive blood from the body and the veins, and the ventricles pump … [Read more...] about Human Heart: Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart
Carb Counting for Diabetes Made Easy Cheat Sheet
A Beginner's Guide/Cheat Sheet to Carbohydrate Counting Use carbohydrate counting to help keep your blood glucose levels in your target range. Carbohydrate Counting & Diabetes For people with diabetes, counting carbohydrates is essential to blood sugar control … [Read more...] about Carb Counting for Diabetes Made Easy Cheat Sheet