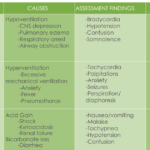
To help you with analyzing ABGs, we have created a cheatsheet that outlines: What lab values you will see with a given ABG finding. What assessment findings you will see. Causes for the abnormality. Possible solutions. … [Read more...] about ABG’s Analysis Cheat Sheet
Nursing Study
NCLEX Pharmacology Antidotes
Must need for your NCLEX exam! Get what you need to know about pharmacology right here: … [Read more...] about NCLEX Pharmacology Antidotes
NCLEX Notes: Types of Diet
TYPES OF DIET A. Regular Diet – pertains to food & fluids that contain all the essential nutrients (CHO, CHON, Fats) necessary for tissue growth, repair, and recovery. B. Clear Liquid Diet – contains water and CHO, but has insignificant amounts of CHON, fats, & other essential nutrients; for short term use only (24 – 36 hours). Purposes: 1. To relieve … [Read more...] about NCLEX Notes: Types of Diet
Nursing Mnemonic: Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Nursing Mnemonic: Metronidazole (Flagyl) … [Read more...] about Nursing Mnemonic: Metronidazole (Flagyl)
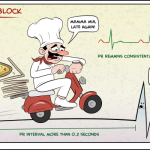
Nursing Study: First Degree Heart Block
Nursing Study: First Degree AV Block In first-degree heart block, the electrical signal is slowed as it moves through the heart. When this occurs between the atria and the ventricles, it appears as a slightly longer, flatter line between the P and the R waves on the EKG. First-degree heart block rarely causes any symptoms. Well-trained athletes and young people are at … [Read more...] about Nursing Study: First Degree Heart Block