A Smarter Way to Interpret ABGs: Better Than ROME or Tic-Tac-Toe!
If you’re a healthcare student or professional trying to make sense of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs), you’ve probably heard of shortcuts like ROME (Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal) or the tic-tac-toe method. But let’s be honest—those tricks often fall short when things get more complex.
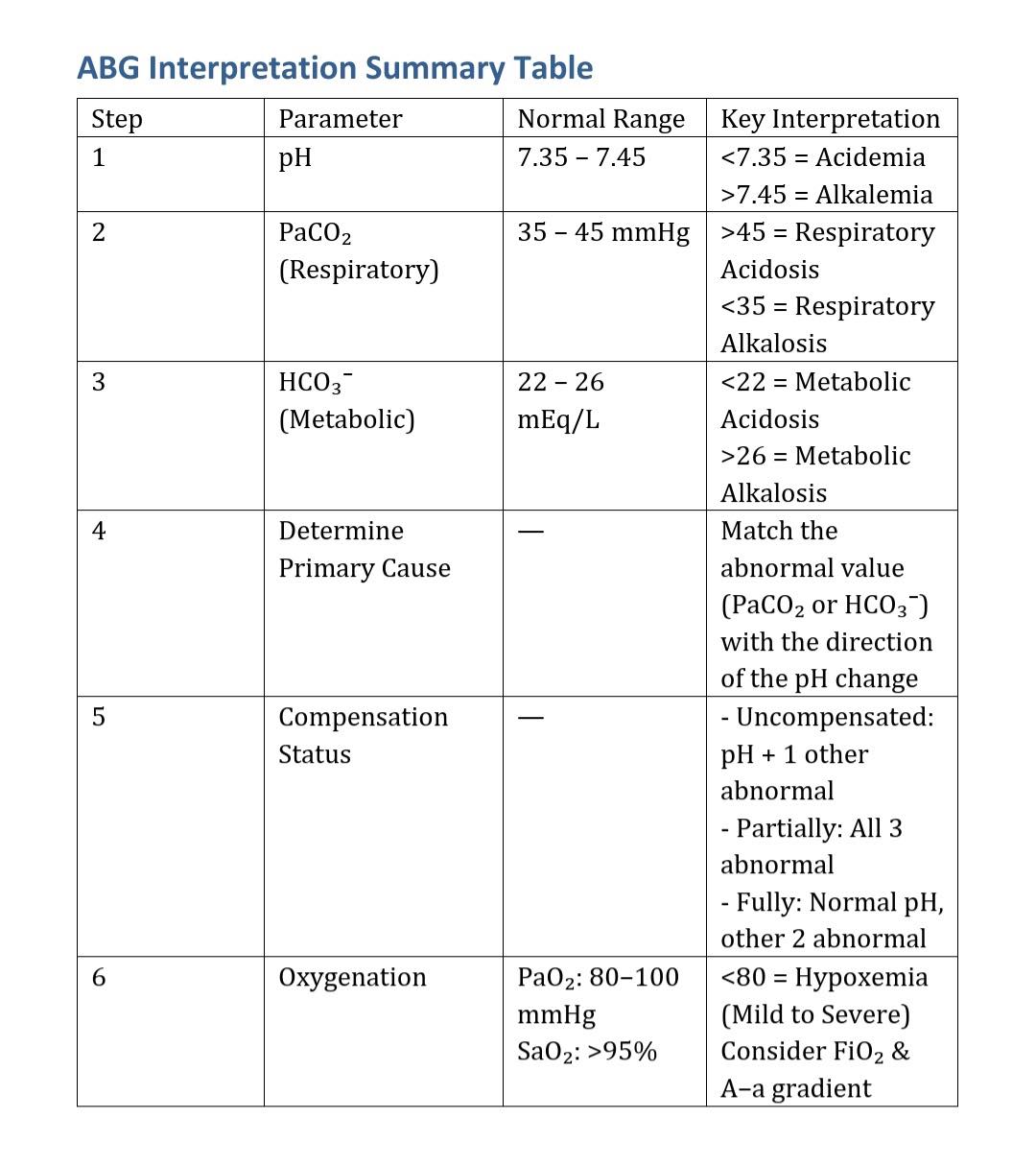
This ABG Interpretation Summary Table is a clear, step-by-step guide that offers more depth and reliability:
🔍 Step-by-Step ABG Analysis
1. Check pH:
- Normal: 7.35–7.45
- <7.35 = Acidemia
- >7.45 = Alkalemia
2. Assess PaCO₂ (Respiratory):
- Normal: 35–45 mmHg
- >45 = Respiratory Acidosis
- <35 = Respiratory Alkalosis
3. Check HCO₃⁻ (Metabolic):
- Normal: 22–26 mEq/L
- <22 = Metabolic Acidosis
- >26 = Metabolic Alkalosis
4. Find the Primary Cause:
Match the abnormal respiratory or metabolic value with the direction of the pH change.
5. Evaluate Compensation:
- Uncompensated: pH + 1 abnormal value
- Partially compensated: All 3 abnormal
- Fully compensated: Normal pH, but other 2 abnormal
6. Check Oxygenation:
- PaO₂: 80–100 mmHg
- SaO₂: >95%
- <80 = Hypoxemia → Evaluate FiO₂ & A-a gradient
This approach doesn’t just help you memorize patterns—it teaches you how to think through the physiology step by step. Whether you’re working in critical care or studying for exams, this method is more accurate, flexible, and clinically useful than older mnemonics.
Ready to ditch shortcuts and start mastering ABGs? Save this table—it’ll be your new go-to!
Leave a Reply